
Geophysical Surveys: Uncovering Secrets in Biblical Archaeology
In the fascinating field of biblical archaeology, geophysical survey methods have emerged as invaluable tools for uncovering hidden secrets and gaining deeper insights into the ancient world. These techniques have revolutionized the way we approach archaeological excavations, leading to significant discoveries and a better understanding of our historical roots.
By utilizing geophysical survey methods, archaeologists can non-invasively map and analyze subsurface features, providing essential information about the layout, structures, and history of ancient sites. This groundbreaking technology allows us to uncover the hidden truths of the past without disturbing the delicate artifacts that lie beneath our feet.
In this article, we will explore the various geophysical survey methods employed in biblical archaeology and highlight their importance in unraveling the mysteries of the past. From ground-penetrating radar (GPR) to magnetometry and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), each method plays a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of ancient civilizations and shedding light on their historical significance.
Key Takeaways:
- Geophysical survey methods are invaluable tools in biblical archaeology, uncovering hidden secrets and providing insights into the ancient world.
- Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) allows for the detection of subsurface structures without the need for excavation.
- Magnetometry helps in mapping ancient settlements and understanding their organization.
- Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) unveils hidden subsurface layers, aiding in the stratigraphy and historical development of archaeological sites.
- By combining geophysical survey methods with traditional excavation techniques, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of ancient civilizations.
Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR): Revealing Subsurface Structures
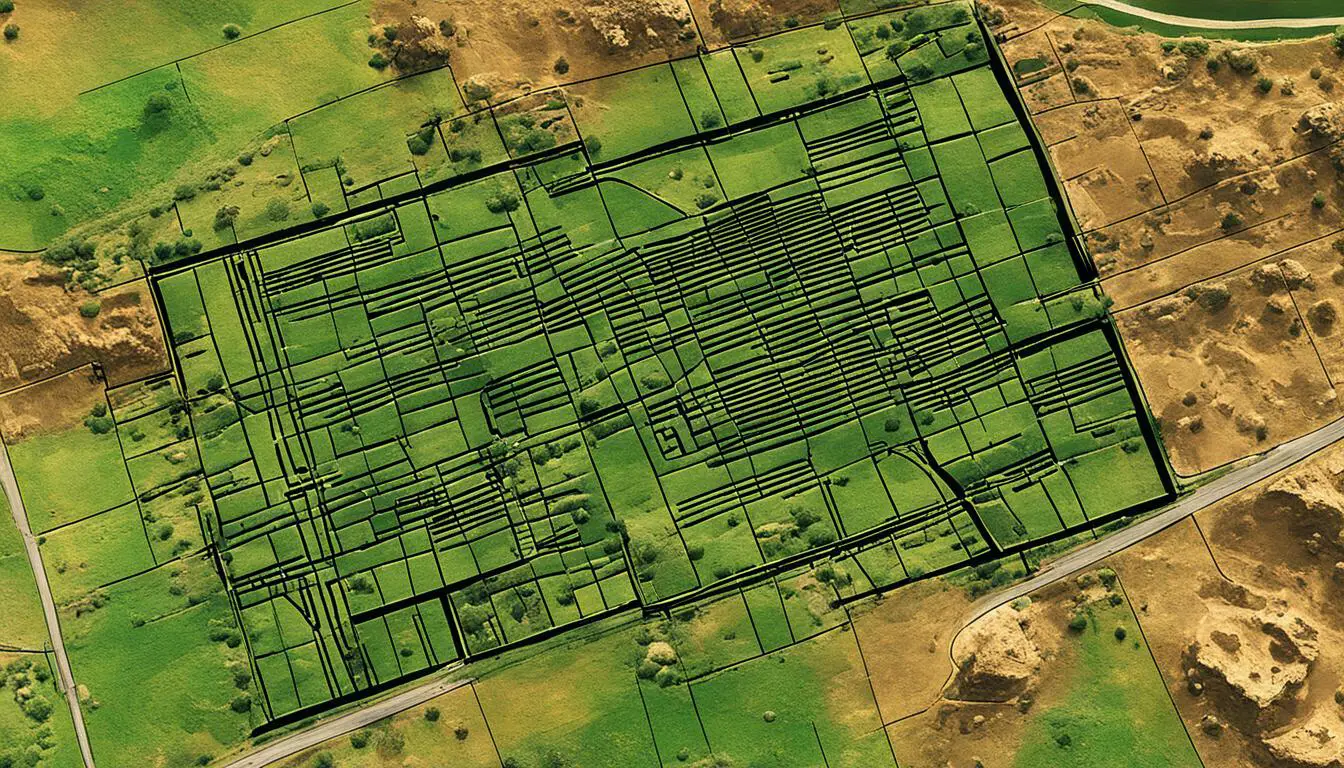
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is an essential geophysical survey method used in biblical archaeology. It allows archaeologists to obtain high-resolution images of subsurface structures without the need for excavation.
By emitting electromagnetic pulses into the ground and measuring the reflected signals, GPR can detect buried features such as walls, foundations, tombs, and even underground chambers. This method provides invaluable information about the layout and organization of ancient sites, aiding in the reconstruction of lost structures and the identification of hidden archaeological features.
In biblical archaeology, GPR has played a significant role in uncovering the mysteries of the past. It has helped researchers map out ancient cities, identify hidden passages and chambers, and even locate long-lost tombs. The ability to visualize subsurface structures in detail has revolutionized our understanding of ancient civilizations and their architectural wonders.
The image above demonstrates the power of ground-penetrating radar in revealing subsurface structures. With its ability to penetrate the ground and provide accurate imaging, GPR has become an indispensable tool for archaeological investigations.
Advantages of Ground-Penetrating Radar in Biblical Archaeology
“Ground-penetrating radar has been a game-changer in our field. It allows us to see beneath the surface and uncover a wealth of information about ancient structures and civilizations. The level of detail provided by GPR is unmatched, and it saves us time and resources that would be spent on extensive excavations.”
The advantages of using GPR in biblical archaeology are numerous:
- Non-invasive: GPR does not require extensive excavation, minimizing potential damage to the archaeological site.
- High-resolution images: The technology of GPR provides clear and detailed images of subsurface structures.
- Efficiency: GPR allows for rapid data acquisition, saving time and resources during archaeological surveys.
- Identification of hidden features: GPR can detect buried walls, foundations, tombs, and underground chambers that may not be visible on the surface.
- Preservation of delicate artifacts: By avoiding unnecessary excavation, GPR helps preserve fragile artifacts.
The table below summarizes some notable discoveries made using ground-penetrating radar in biblical archaeology:
| Discovery | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| The underground city | Jerusalem, Israel | GPR revealed an expansive network of subterranean tunnels and chambers beneath the city, shedding light on ancient urban planning and defensive strategies. |
| Hidden temple complex | Temple Mount, Jerusalem | GPR uncovered a hidden temple complex with multiple chambers and elaborate architectural features, providing insights into religious practices. |
| The lost burial ground | Gethsemane, Jerusalem | GPR detected a previously unknown burial ground beneath the surface, offering new information about burial customs and traditions. |
Through the use of ground-penetrating radar, biblical archaeologists continue to make groundbreaking discoveries that deepen our understanding of ancient civilizations and bring the stories of the past to life.
Magnetometry: Mapping Ancient Settlements
Magnetometry is another geophysical survey method widely employed in biblical archaeology for mapping ancient settlements. This technique measures and records variations in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by human activities, such as the presence of burnt structures, kilns, or buried artifacts.
By using highly sensitive magnetometers, archaeologists can create detailed magnetic maps that highlight areas of archaeological interest. These maps help to identify structures, distinguish between different occupation periods, and understand the organization of ancient settlements.
Magnetometry is particularly useful in detecting hidden features that might not be visible on the surface, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the past.
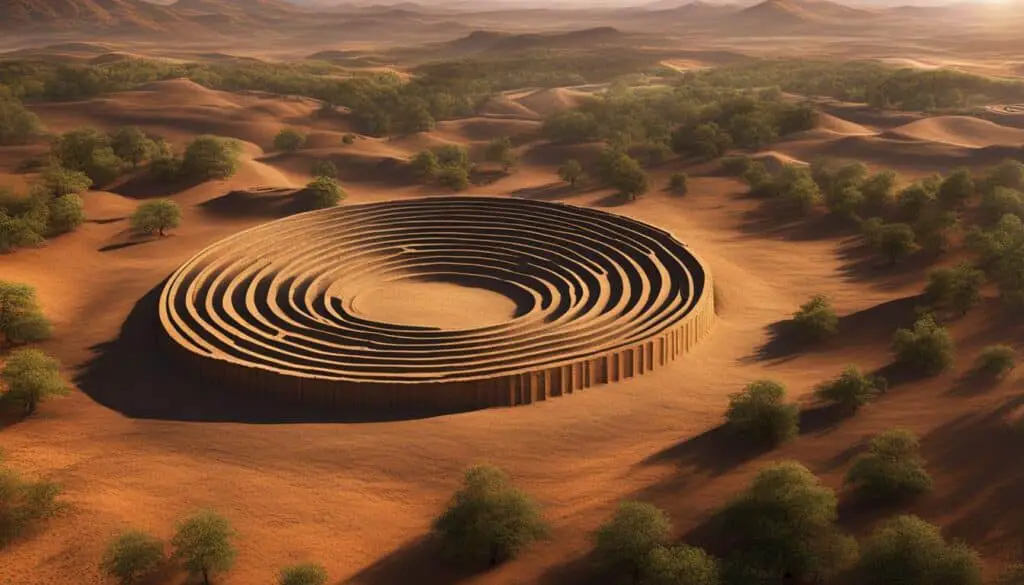

Using magnetometry, archaeologists can visualize the buried remnants of buildings, walls, and other significant features that have been obscured by time and natural processes. The variations in the magnetic field strength are mapped and plotted, revealing the layout and extent of ancient settlements.
Magnetometry is a powerful tool in biblical archaeology, enabling us to explore the hidden world of ancient settlements. By identifying the magnetic signatures left by human activities, we can unravel the secrets of the past and gain invaluable insights into the lives and societies of our ancestors.
Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT): Unveiling Subsurface Layers
Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) is a geophysical survey method commonly used in biblical archaeology to reveal subsurface layers. By measuring the electrical resistance of the ground at different depths, ERT provides valuable insights into hidden structures, geological formations, and buried artifacts. The variation in resistivity between different materials, such as stone walls or filled-in ditches, creates a contrast that can be analyzed to generate 2D or 3D images. These images help archaeologists understand the stratigraphy of an archaeological site and gain a deeper understanding of its historical development.
ERT plays a crucial role in mapping the subsurface layers and identifying significant features that may not be visible on the surface. This method allows archaeologists to uncover hidden secrets buried beneath the soil, providing a more comprehensive understanding of ancient civilizations and their way of life.
Advantages of Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
- Non-invasive: Unlike traditional excavation methods, ERT allows for the non-destructive mapping of subsurface layers.
- High-resolution imaging: ERT provides detailed 2D or 3D images that capture the intricate features of hidden structures.
- Cost-effective: By minimizing excavation, ERT helps archaeologists save time and resources.
- Wide range of applications: ERT can be used to study a variety of archaeological sites, from ancient settlements to religious complexes, providing valuable insights into different periods of history.
The use of electrical resistivity tomography has revolutionized biblical archaeology, enabling researchers to piece together the puzzle of the past by uncovering the secrets hidden beneath the surface. By leveraging this powerful geophysical survey method, archaeologists can delve deeper into the history of ancient civilizations, gaining a more comprehensive understanding of their achievements, social structures, and cultural practices.
| Geophysical Survey Method | Main Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) | – Mapping subsurface structures – Locating buried tombs or chambers |
– Non-invasive imaging – High-resolution detection |
| Magnetometry | – Mapping ancient settlements – Identifying buried artifacts |
– Wide coverage area – Ability to detect hidden features |
| Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) | – Unveiling subsurface layers – Understanding stratigraphy |
– Non-invasive imaging – Detailed 2D/3D visualization |
Conclusion
Geophysical survey methods have revolutionized the field of biblical archaeology, enabling researchers to unlock hidden secrets and gain a deeper understanding of the ancient world. Techniques such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), magnetometry, and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) have become invaluable tools in non-invasive mapping, uncovering ancient settlements, and revealing hidden layers of the past.
By combining these geophysical survey methods with traditional excavation techniques, archaeologists can paint a more comprehensive picture of ancient civilizations and unearth untold stories buried beneath the surface. The ability to non-invasively map subsurface structures, detect hidden features, and analyze subsurface layers has led to significant discoveries in biblical archaeology.
Geophysical surveys continue to play a crucial role in shedding light on history, religion, and the lives of ancient peoples. These methods have reshaped the way we approach archaeological excavations and have provided researchers with essential information about the layout, structures, and history of ancient sites. Through geophysical survey methods, the mysteries of biblical archaeology are being uncovered, offering valuable insights into our shared human history.
FAQ
What is geophysical survey?
Geophysical survey is a method used in biblical archaeology to non-invasively map and analyze subsurface features, providing essential information about the layout, structures, and history of ancient sites.
How does ground-penetrating radar (GPR) work?
Ground-penetrating radar emits electromagnetic pulses into the ground and measures the reflected signals to detect buried features such as walls, foundations, tombs, and underground chambers.
What can be detected using magnetometry?
Magnetometry can detect variations in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by human activities, helping to identify structures, distinguish between different occupation periods, and understand the organization of ancient settlements.
How does electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) unveil subsurface layers?
Electrical resistivity tomography measures the electrical resistance of the ground at different depths, generating 2D or 3D images that reveal the presence of hidden structures, geological formations, or buried artifacts.
What role do geophysical survey methods play in biblical archaeology?
Geophysical survey methods have revolutionized biblical archaeology by allowing researchers to uncover hidden secrets and gain a deeper understanding of the ancient world.
