
Lidar technology has revolutionized the field of archaeology, allowing us to discover and study ancient biblical cities like never before. Through advanced laser scanning techniques, lidar enables researchers to create detailed 3D maps of archaeological sites and detect hidden structures and features that were previously unseen. This groundbreaking technology has been instrumental in uncovering and understanding ancient civilizations mentioned in the Bible.
With lidar, we can now explore ancient cities that have long been buried beneath layers of time and history. This technology has opened new avenues for archaeologists to piece together the past, bringing us closer to the people, cultures, and stories described in ancient texts.
Key Takeaways:
- Lidar technology has revolutionized archaeology, enabling the discovery and study of ancient biblical cities.
- Through laser scanning, lidar creates detailed 3D maps and reveals hidden structures in archaeological sites.
- Unearthing biblical cities with lidar provides valuable insights into ancient civilizations mentioned in the Bible.
- Lidar technology allows researchers to explore buried ancient cities, contributing to our understanding of the past.
- By combining lidar data with other geospatial datasets, we can create comprehensive archaeological maps and databases.
What is Lidar Technology?
Lidar, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that utilizes lasers to measure distances and create detailed models of the Earth’s surface. Through the process of laser scanning, lidar systems emit laser pulses and accurately measure the time it takes for the light to bounce back after hitting an object. By analyzing the reflected laser data, lidar technology can generate highly precise and high-resolution maps of various landscapes, including archaeological sites.
Lidar technology operates on the principle of remote sensing, enabling the scanning and mapping of extensive areas without physical contact. Its applications extend beyond archaeology, finding utility in fields such as forestry, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
“Lidar technology has revolutionized the way we explore and understand the world around us. By capturing detailed and accurate data from a distance, lidar allows us to uncover hidden features and gain new insights into ancient civilizations and archaeological sites.”
With laser scanning as its foundation, lidar’s capabilities in the context of archaeology are particularly significant. It empowers researchers to precisely ascertain the topography of ancient landscapes and unmask structures that may have remained hidden for centuries.
The Laser Scanning Process
The laser scanning process involves several key steps:
- The lidar device emits laser pulses towards the Earth’s surface.
- The laser pulses strike objects or structures on the ground, such as buildings, trees, or archaeological remains.
- The light energy of the laser pulses bounces back to the lidar system.
- The lidar system records the time it takes for the laser pulses to return.
- By analyzing the time delay, the lidar system calculates the distance between the emitter and the struck object.
The captured data is then meticulously processed and transformed into accurate and detailed 3D models of the scanned area. These models provide invaluable insights into the terrain, morphology, and potential archaeological features of the site.
Advantages of Lidar Technology
Lidar technology offers numerous advantages in the field of archaeology:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Lidar accurately measures distances and creates highly detailed models, providing archaeologists with precise data for analyses and visualizations.
- Rapid Data Collection: Lidar systems can quickly scan large areas, significantly accelerating the survey process and minimizing the need for time-consuming manual measurements.
- Remote Sensing Capabilities: Lidar’s ability to penetrate vegetation and capture data from beneath the forest canopy makes it invaluable for surveying challenging or inaccessible archaeological sites.
- Non-Invasive Approach: Lidar technology allows archaeologists to study sites without causing physical damage, preserving the integrity of the historical remains.
These advantages make lidar an indispensable tool in archaeological research, enabling the exploration of historical landscapes and aiding in the identification of potential areas for excavation.
| Advantages of Lidar Technology in Archaeology |
|---|
| Enhanced Accuracy |
| Rapid Data Collection |
| Remote Sensing Capabilities |
| Non-Invasive Approach |
Lidar Technology in Archaeology
Lidar technology plays a crucial role in the field of archaeology, offering researchers a powerful tool for studying and analyzing archaeological sites. By utilizing lidar scanners mounted on aircraft or ground-based vehicles, archaeologists can efficiently scan large areas and generate detailed digital elevation models, revolutionizing the way we explore and understand ancient civilizations.
Enhancing Site Identification and Excavation
One of the key advantages of lidar technology in archaeology is its ability to identify potential sites for excavation. By creating accurate and detailed maps of the topography, lidar can help archaeologists pinpoint areas of interest and plan their excavation strategies more effectively. This saves valuable time, resources, and minimizes the need for extensive and invasive ground surveys.
Furthermore, lidar technology allows archaeologists to uncover hidden structures and features that are invisible to the naked eye. By analyzing the data captured by lidar scanners, researchers can detect subtle variations in the terrain that may indicate the presence of ancient structures, such as walls, buildings, or even entire settlements. This valuable information guides excavations and provides a deeper understanding of the layout and organization of archaeological sites.
Mapping Ancient Landscapes
Lidar technology also enables archaeologists to create detailed maps of ancient landscapes, providing valuable insights into the archaeological context of specific areas. By generating accurate digital elevation models, lidar reveals the natural and artificial features of the terrain, including changes in elevation, vegetation coverage, and waterways. This information helps archaeologists understand how ancient civilizations interacted with their environment, providing clues about their agricultural practices, trade routes, and settlement patterns.
| Benefit of Lidar Technology in Archaeology | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficient and Accurate Scanning | Lidar scanners quickly capture vast amounts of data with high precision, allowing archaeologists to cover larger areas in less time. |
| Improved Visualization and Analysis | The detailed 3D models created by lidar technology facilitate better visualization and analysis of archaeological sites, aiding in the interpretation of findings. |
| Non-Invasive Data Collection | Lidar technology minimizes the need for invasive ground surveys, reducing the risk of damage to archaeological sites and artifacts. |
| Uncovering Hidden Features | Lidar can reveal hidden structures and features that are not visible from the surface, shedding light on the complexity and extent of ancient civilizations. |
Overall, lidar technology has transformed the way we approach archaeological research, providing archaeologists with invaluable insights into the past. By utilizing lidar scanners, researchers are able to identify potential excavation sites, map ancient landscapes, and uncover hidden structures and features. This technology not only enhances our understanding of ancient civilizations but also opens up new avenues for future archaeological discoveries.
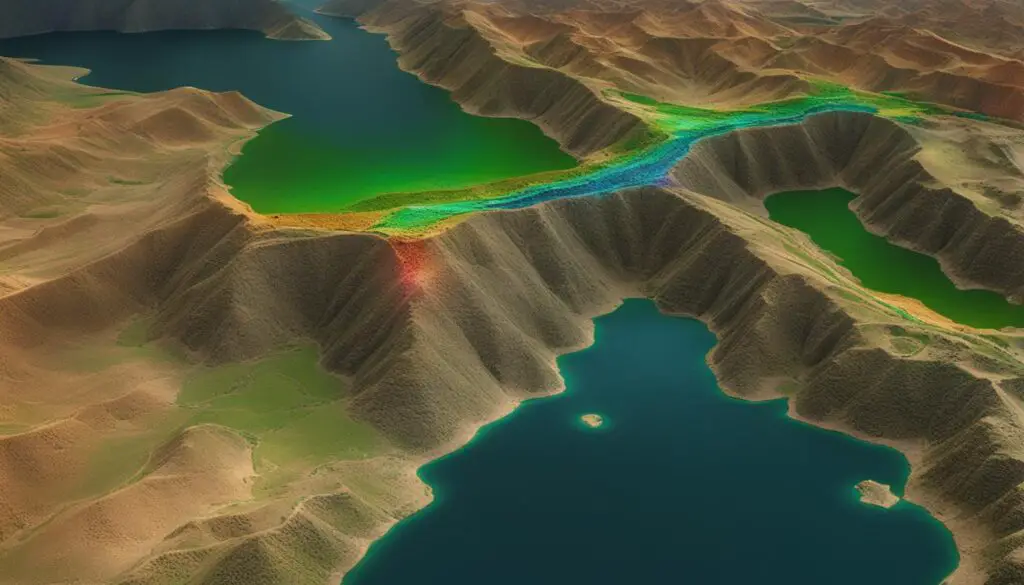
Unearthing Biblical Cities with Lidar
Lidar technology has played a crucial role in the unearthing and understanding of biblical cities mentioned in ancient texts. Its advanced laser scanning techniques have allowed archaeologists to reveal hidden structures and settlements that correspond to ancient biblical cities mentioned in the Old and New Testaments.
One notable example of lidar’s impact is the discovery of a previously unknown ancient Mayan city in Guatemala in 2018. A team of archaeologists utilized lidar scans to identify the hidden remains of this ancient civilization. This groundbreaking find not only expanded our knowledge of Mayan history but also showcased the power of lidar technology in uncovering past civilizations.
Furthermore, lidar scans of sites in the Near East have provided valuable insights into ancient biblical cities. By analyzing the data obtained through lidar technology, historians and archaeologists have gained new perspectives on the lives, cultures, and structures of these ancient civilizations.
“Lidar technology has opened up a world of possibilities for archaeologists. It has allowed us to literally see beyond what was previously hidden, revealing ancient cities and settlements that were lost to time,” shared Dr. Sarah Thompson, an archaeologist specializing in ancient civilizations.
The Role of Lidar in Historical Mapping and Preservation
Lidar technology not only helps in the discovery and exploration of biblical cities but also plays a crucial role in historical mapping and preservation. By creating detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, lidar scans aid in documenting the current state of these ancient cities and tracking changes over time. This information is invaluable for conservation efforts and archaeological research.
Furthermore, the high-resolution mapping capabilities of lidar enable researchers to accurately measure and record the locations and dimensions of architectural features, such as buildings, temples, and walls. This data helps reconstruct the ancient cityscapes and provides a deeper understanding of the urban planning and construction techniques employed by ancient civilizations.
Lidar’s Impact on the Study of Ancient Civilizations
The use of lidar technology in the study of biblical cities and ancient civilizations has revolutionized the field of archaeology. This powerful tool enables researchers to gather detailed and accurate data on the layouts and structures of these ancient cities, shedding light on their cultural practices, social dynamics, and religious beliefs.
By leveraging the insights gained from lidar scans, historians and archaeologists can develop comprehensive narratives of ancient civilizations, bringing their stories to life. The combination of lidar data with historical texts and artifacts allows for a more holistic understanding of the past, providing a deeper appreciation of the rich and diverse tapestry of human history.
The Future of Lidar Technology in Archaeology
The future implications of lidar technology in archaeology are incredibly promising. As lidar scanners become smaller, more affordable, and easier to use, researchers from around the world will have increased access to this revolutionary tool. This accessibility will undoubtedly lead to more discoveries of biblical cities and ancient civilizations, further enriching our understanding of the past.
Moreover, the integration of lidar data with other geospatial datasets, such as satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), will enable researchers to create comprehensive archaeological maps and databases. This interdisciplinary approach holds immense potential for uncovering hidden connections, revealing patterns across civilizations, and advancing archaeological research.

| Advantages of Lidar Technology in Archaeology |
|---|
| 1. Non-invasive surveying of large areas |
| 2. Penetration of dense vegetation for studying tropical regions |
| 3. Creation of detailed 3D models aiding visualization and analysis |
Advantages of Lidar Technology in Archaeology
Lidar technology offers several advantages in the field of archaeology. Firstly, lidar allows archaeologists to quickly and non-invasively survey large areas, saving time and resources compared to traditional excavation methods. By using lidar scanners mounted on aircraft or ground-based vehicles, researchers can cover vast territories in a fraction of the time it would take to excavate each site individually. This efficiency is particularly valuable when dealing with extensive landscapes or time-sensitive projects.
Secondly, lidar can penetrate dense vegetation and capture data from beneath the forest canopy, making it especially useful for studying archaeological sites in tropical regions or areas with overgrown vegetation. Traditional survey techniques might struggle to provide accurate data in these environments, but lidar’s laser pulses can effectively reach the ground surface, providing comprehensive coverage and revealing hidden features that may have been obscured by dense foliage.
Lastly, lidar’s high-resolution mapping capabilities enable researchers to create detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, aiding in visualization and analysis. The precise data collected by lidar scanners allows for the creation of accurate and realistic representations of the site, providing a valuable tool for studying and understanding the structures, landscapes, and other features that form part of the archaeological record. These 3D models also facilitate collaboration and communication among researchers, allowing for a deeper exploration of the site and the artifacts it holds.
Overall, lidar technology’s ability to efficiently survey large areas, penetrate vegetation, and provide high-resolution mapping has greatly advanced the field of archaeology. It offers invaluable assistance in identifying potential sites, revealing hidden features, and creating detailed visualizations, ultimately contributing to a better understanding of our past.
Future Implications of Lidar Technology in Archaeology
The future of lidar technology in archaeology holds great promise. With ongoing advancements, lidar scanners are becoming smaller, more affordable, and increasingly accessible to researchers worldwide. This evolution makes lidar a potent tool for unearthing ancient civilizations and revealing hidden historical treasures.
The integration of lidar data with other geospatial datasets, such as satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), further enhances its potential. By combining these technologies, archaeologists can create comprehensive archaeological maps and databases, enabling a more holistic understanding of the past. This multi-dimensional approach offers unprecedented opportunities for groundbreaking discoveries and new insights into the mysteries of ancient civilizations.
As lidar technology becomes more refined and widely adopted in the field of archaeology, its implications for future research are abundant. By employing this cutting-edge tool, archaeologists can explore uncharted territories, unravel the secrets of buried cities, and reconstruct ancient landscapes with unprecedented accuracy. Lidar’s ability to penetrate dense vegetation and capture hidden features will prove invaluable in unlocking the rich history of civilizations that have long been obscured from human sight.
Conclusion
Lidar technology has revolutionized the field of archaeology, allowing us to uncover the secrets of ancient biblical cities and gain a deeper understanding of ancient civilizations. Through its advanced laser scanning techniques, lidar has provided archaeologists with the ability to create detailed 3D maps of archaeological sites, revealing hidden structures and features that were once invisible to the naked eye.
By harnessing the power of lidar, researchers have made remarkable discoveries, shedding new light on the civilizations mentioned in the Bible. From the unearthing of a previously unknown ancient Mayan city in Guatemala to the identification of hidden settlements corresponding to biblical cities in the Near East, lidar has proven to be an invaluable tool in uncovering our ancient past.
As lidar technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in the field of archaeology. Smaller, more accessible lidar scanners are emerging, allowing researchers from around the world to utilize this powerful tool. By combining lidar data with other geospatial datasets, such as satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), researchers are able to create comprehensive archaeological maps and databases, further enriching our knowledge of ancient civilizations.
In conclusion, lidar technology has transformed the way we study and unearth ancient biblical cities. Through its ability to provide detailed and accurate 3D maps, lidar has opened up new possibilities for archaeological research. With its ongoing advancements, lidar holds the potential to make even more groundbreaking discoveries, revolutionizing our understanding of ancient civilizations and the stories they hold.
FAQ
How does lidar technology work?
Lidar technology uses lasers to measure distances and create detailed models of the Earth’s surface. It works by sending out laser pulses and analyzing the reflected data to generate accurate maps.
How is lidar technology used in archaeology?
Lidar technology is used in archaeology to study and analyze archaeological sites. It allows researchers to quickly scan large areas, map out ancient landscapes, and identify hidden structures and features.
What role does lidar technology play in unearthing biblical cities?
Lidar technology has played a crucial role in discovering and understanding biblical cities mentioned in ancient texts. It has helped reveal hidden structures and settlements that correspond to these ancient cities.
What are the advantages of lidar technology in archaeology?
Lidar technology offers several advantages in archaeology, including non-invasive surveying of large areas, penetration of dense vegetation, and high-resolution mapping for detailed 3D models.
What does the future hold for lidar technology in archaeology?
The future of lidar technology in archaeology looks promising. As the technology continues to advance, it will become more accessible and integrated with other geospatial datasets, leading to further discoveries and advancements in the field.








